We tested a transcutaneous core temperature sensor using a method that relies on the principle of zero heat flow. Low admission temperature is an independent risk factor for morbidity and mortality in preterm infants1 thermal stability is enhanced by use of polythene bags during stabilisation2 but it has been suggested that this may induce potentially harmful hyperthermia3 we have measured the changes in body temperature during the first 15 minutes after birth in infants stabilised in polythene bags.
Cardiorespiratory Events In Preterm Infants Etiology And
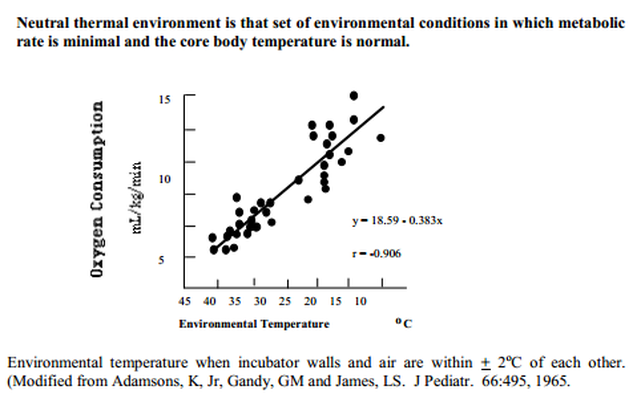
Measurement of core body temperature in preterm infants. Preterm infants possess a disproportionate body mass to surface area ratio reduced thermal insulation in decreased brown adipose tissue bat a thin epidermis that has increased permeability poor vasomotor control and a naturally extended position that exposes a greater body surface area to the external environment. Neonatal network jsmith 40 galcock 20 agardner 10 kusher 30 h index 400 chapter 3 concordance of temperature measurements in the preterm and term neonate using three thermometers under review in. 69 temperature measurement was conducted continuously mostly by using a skin probe either attached to the backlying surface 43 or to the anterior abdomen of the infant 28rectal probes were less frequently used for continuous temperature monitoring 8. Many common procedures and care expose these premature infants to cold environ. An inadequate body temperature in preterm infants influences morbidity and mortality. Hull smales 1978.
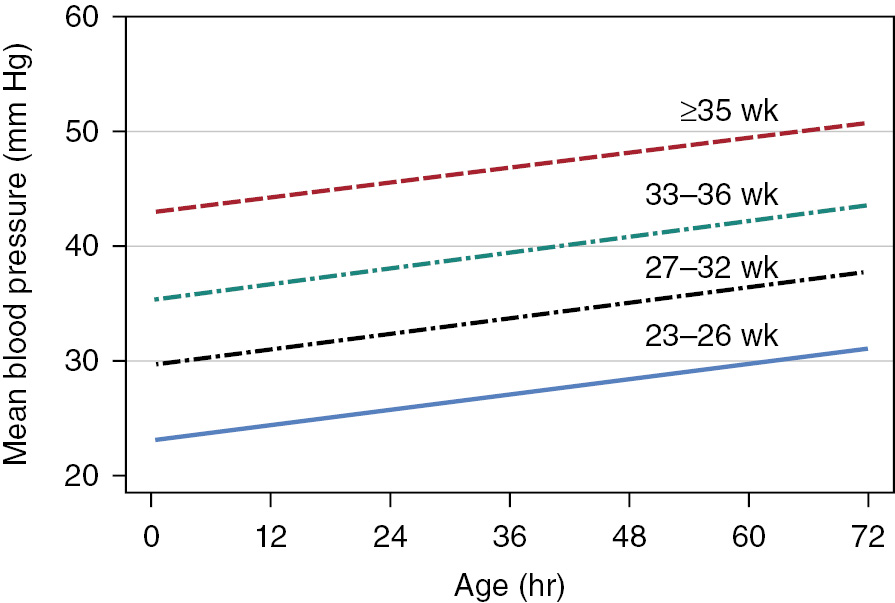
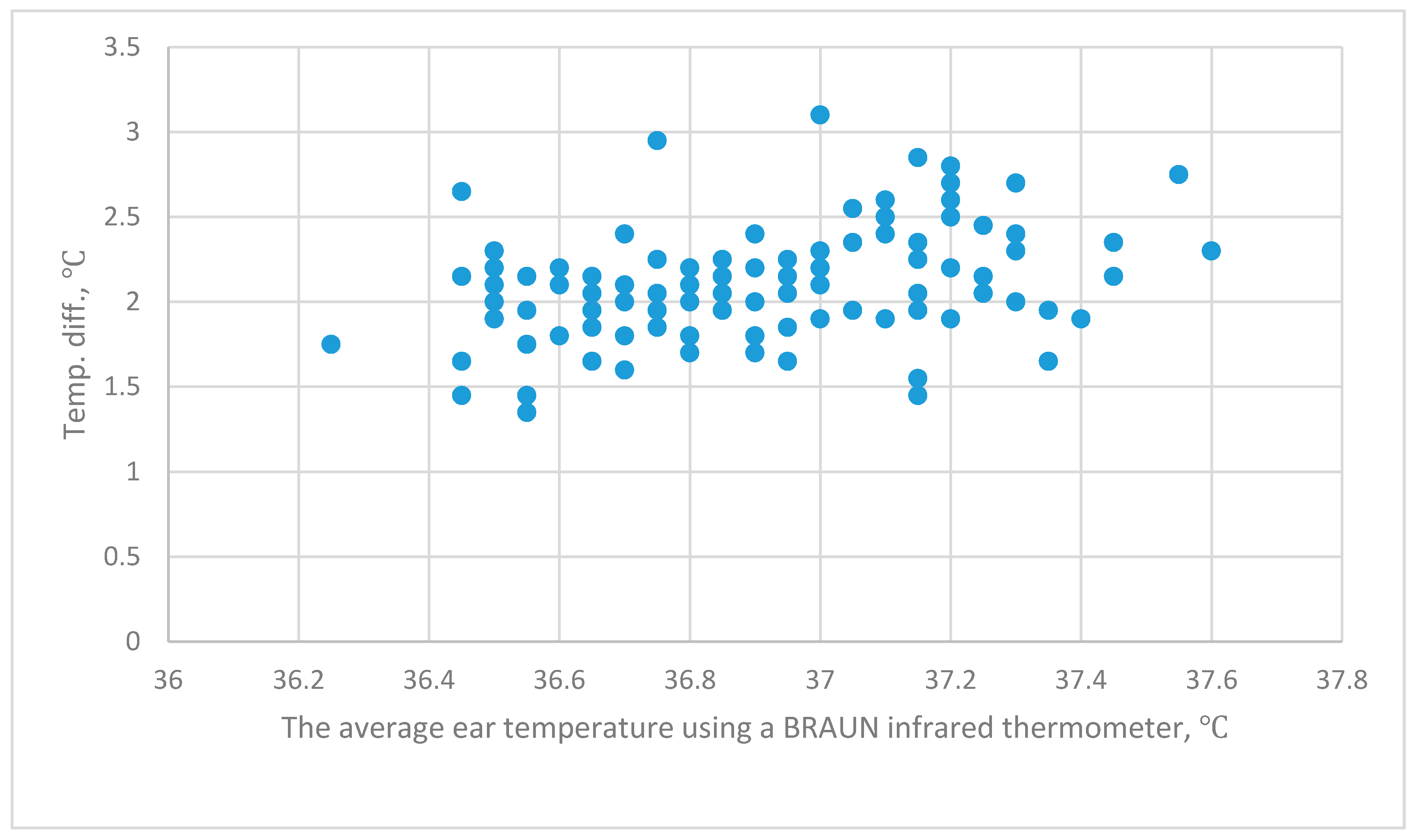
Axillary temperature was as reliable as rectal temperature measured in the usual way with a mercury in glass thermometer. A review of the literature in press in. Gradient measurement measuring the gradient between the central and peripheral body. During this period body temperature is highly dependent on the environmental temperature and its surroundings. In the majority of centers n 60. We designed a study for 30 infants to examine body temperature over their first week of life to determine when an infant has a mature ability to regulate temperature centrally and peripherally.
1department of neonatology lis maternity hospital tel aviv sourasky medical center israel. Continuous measurement of core body temperature in preterm infants. Dollberg s1 rimon a atherton hd hoath sb. In this article we describe the instrumentation tested and analytic models developed through pilot testing of four elbw infants see table 1 in a case study approach to refine methods for use in the. Chapter 2 temperature measurement in the preterm and term infant. As a result elbw infants are prone to decreases in body temperature.
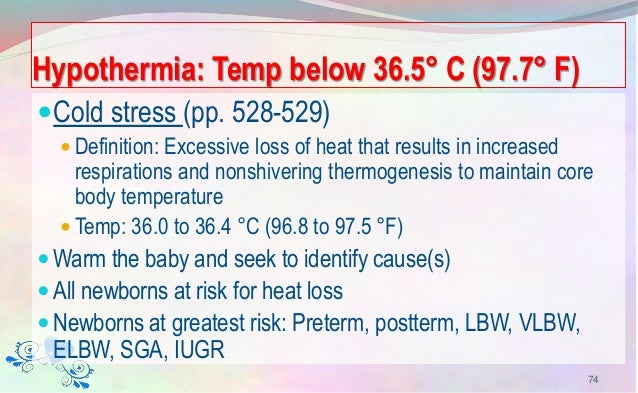
The temperatures in preterm infants were lower and varied less with the site of measurement indicating a smaller core surface temperature gradient because of their relative lack of thermal insulation by body fat. Predisposing factors for hypothermia especially in the premature infant include a large surface area to body mass ratio wet at birth skin immaturity and prematurity. Continuous rectal measurement is a reliable method to measure body temperature but might have adverse effects. Collegian jsmith 40 g. Tle to no ability to maintain core body tempera ture by nonshivering thermogenesis because of an immature thermoregulatory system houstek et al 1993.